Amphibians Breathe Through Skin

Through Body Wall or Skin.
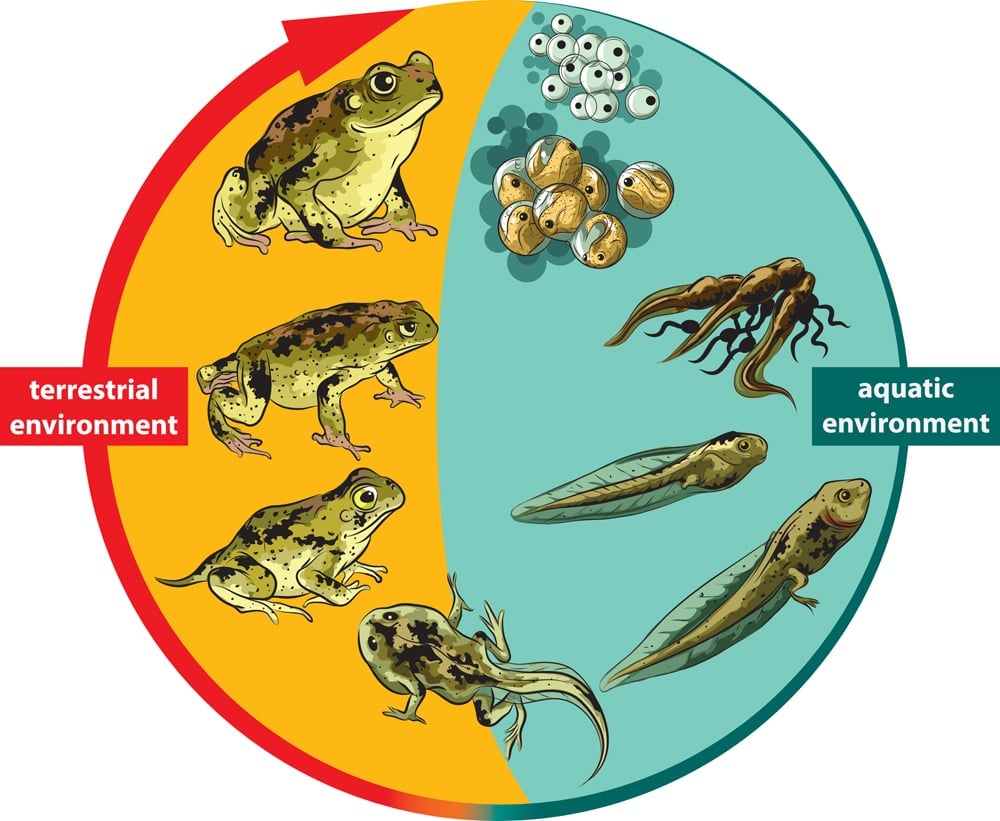
Amphibians breathe through skin. Being thinner and more breathable the epidermis of amphibians puts them at the mercy of the environment completely and they risk dying from dehydration if they dont have a source of water nearby. As amphibian larvae develop the gills and in frogs the. In unicellular animals such as amoeba exchange of gases takes place through cell surface.
Salamanders frogs and toads. Most breathe both through their skin and lungs. Amphibians such as frogs use more than one organ of respiration during their life.
Their skin has to stay wet in order for them to absorb oxygen so they secrete mucous to keep their skin moist If they get too dry they cannot breathe and will die. Unlike reptiles birds and mammals unborn or unhatched amphibians do not develop in a special protective sac called an amniotic sac. Most amphibians have thin skin that is very permeable allowing liquids and gases to pass through it easily.
Cutaneous respiration occurs in a wide variety of organisms including insects. Second it means that amphibians lose a lot of water through their skin. All amphibians including this frog can breathe through their skin as adults.
In reality there are few amphibians that can exist in salt water because their skin is very permeable and the toads have a warty. They breathe through gills while they are tadpoles. There are lungless salamanders that have neither lungs nor gills They just breathe through their skin.
Laevis tadpoles and axolotls have both gills and lungs and will gulp air at the waters surface. With some amphibians it appears that they can breathe underwater when in fact they are holding their breath. However some adult amphibians breathe only through their skin and are lungless.