Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

This structure can even be called the inner membrane to distinguish it from the outer membrane present in gram-negative bacteria.
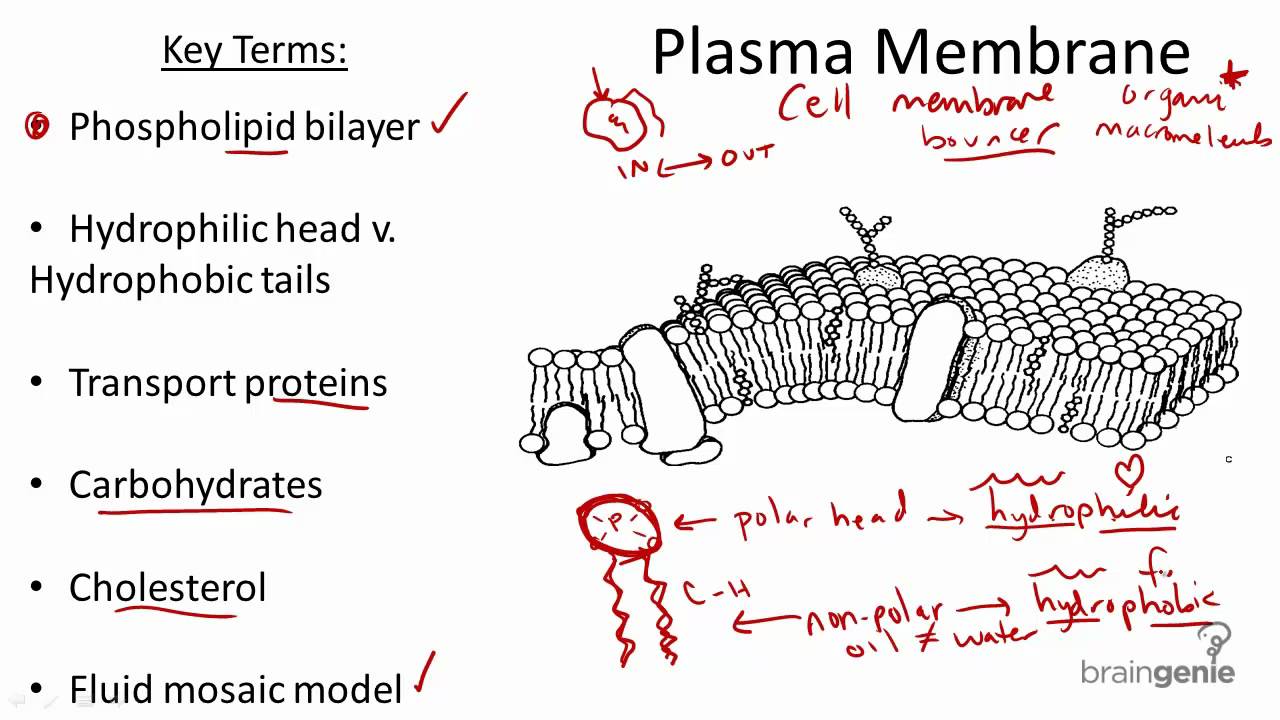
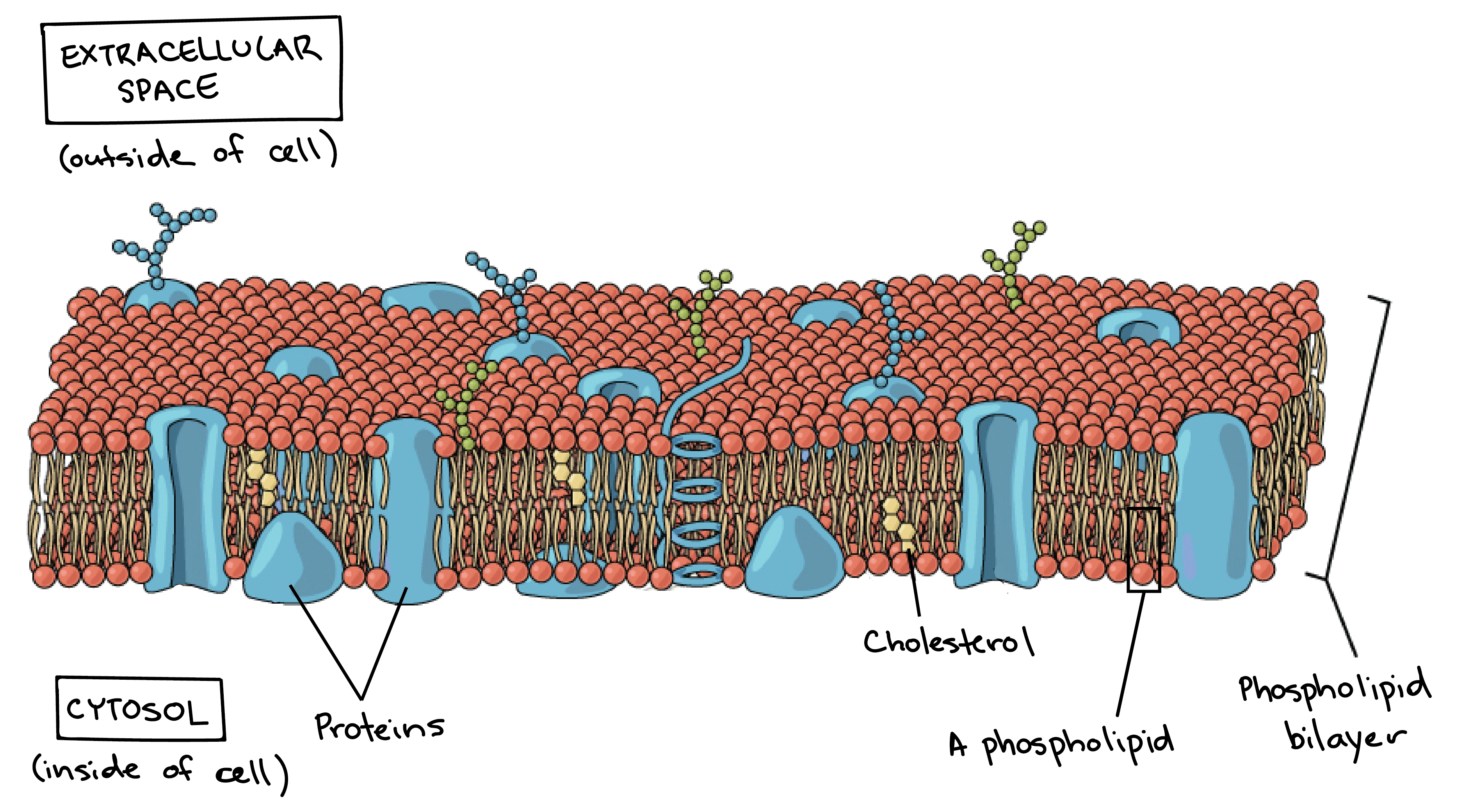
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Organisms are composed of cells and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment which protects the cell from its environment.
The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm. The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes.
Every cell has a lipid and protein layer called cell membrane or cytoplasmic or plasma which defines its boundaries and regulates molecular exchanges with the external environment. The liquid where all. Holds the cell content controls the insouts structural forms cell recognition adhesion signaling transport of substances endoexocytosis Cytoplasm.
Form the basic structure of the membrane phospholipid bilayer The tails form a hydrophobic core comprising the innermost part of both the outer and inner layer of the membrane. Much of the membrane is made up of a sea of phospholipids with protein molecules floating in between the phospholipids. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cells shape.
The plasma membrane is impermeable to ions and most water-soluble molecules. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes. All membranes in a cell have the same basic structure which compartmentalises organelles from its external environment.
The membrane is examined in detail later. Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell.