Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP.
Cellular respiration formula explained. Chemical structures of nad and nadh. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as.
A short video covering the topic of cellular respiration including the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration prepared for a year 9 science. Respiration is of two types aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
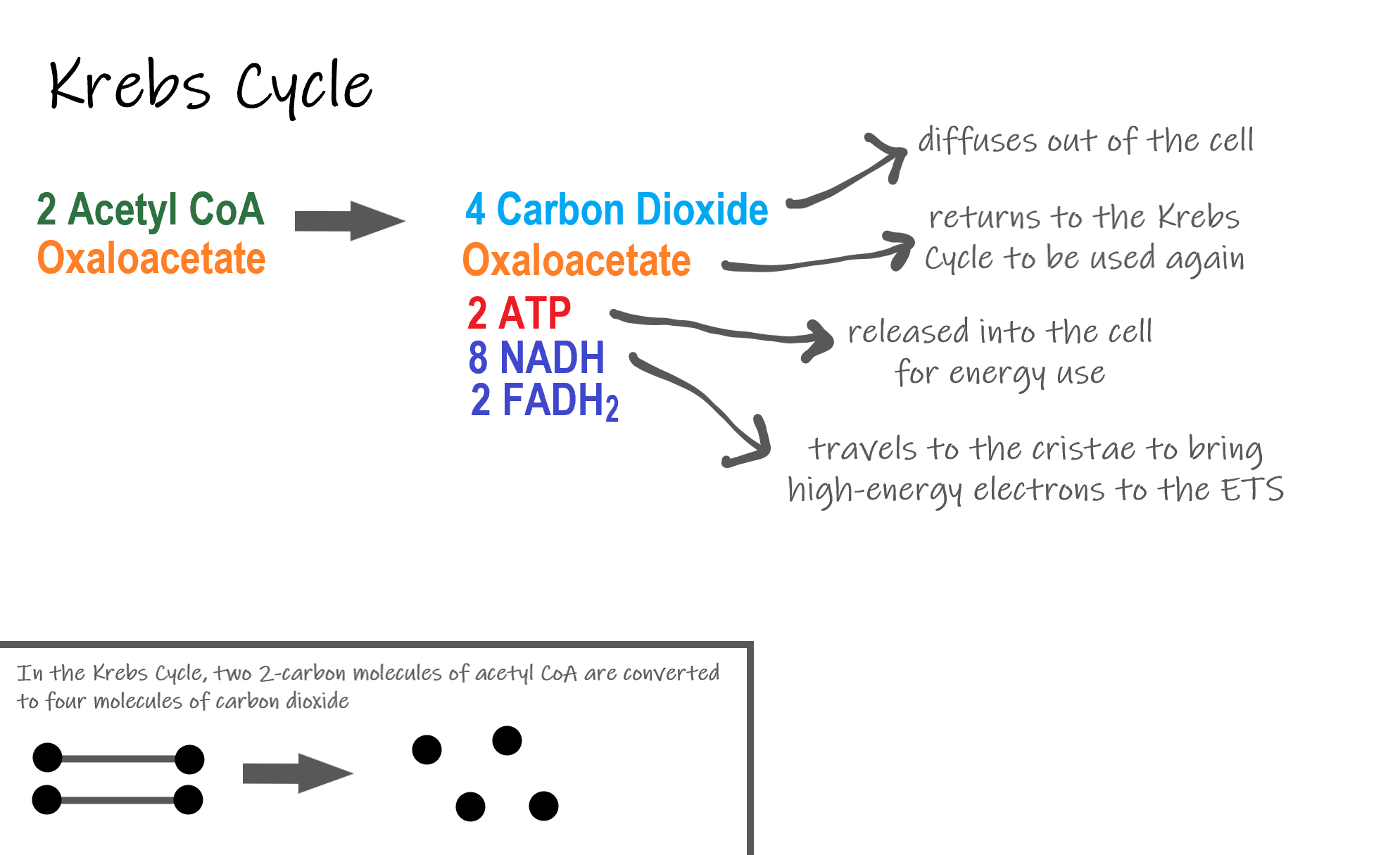
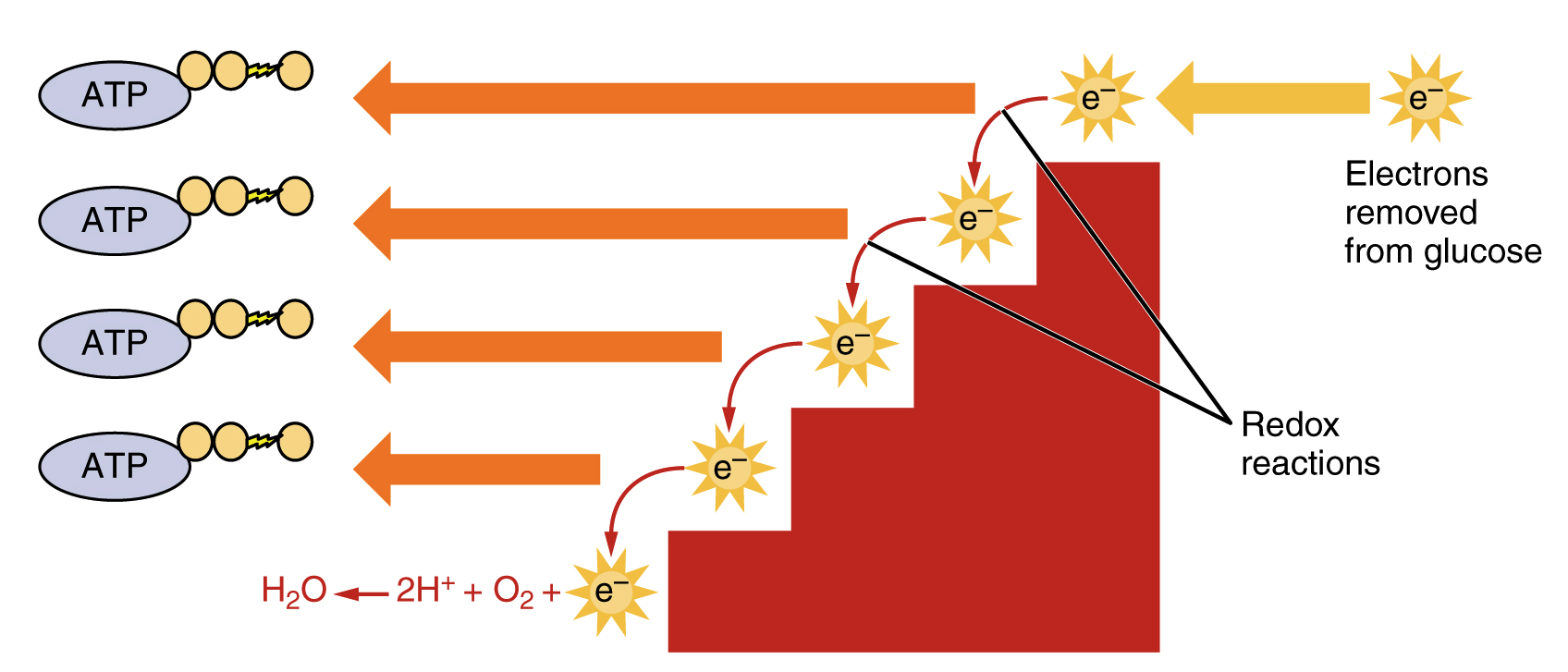
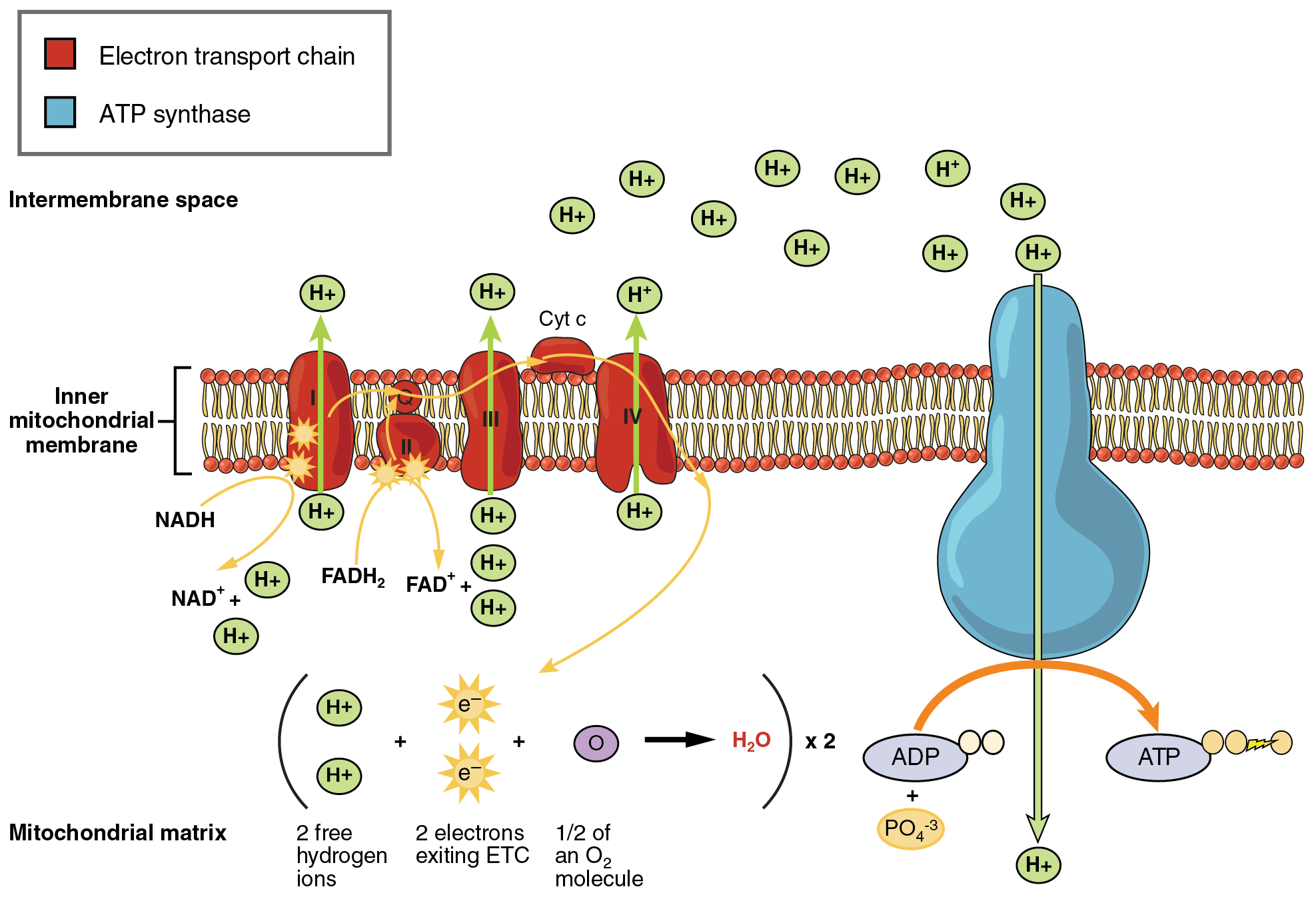
Cellular respiration is a common process that is carried out by many organisms to make and release energy. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy.
C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration. Glucose oxygen chemical energy carbon dioxide water Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp a chemical which the cell uses for energy. In summary cellular respiration is a process that cells use to make energy.
C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6 Oxygen 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water ATP. Living active or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. Cellular respiration formula explained.
Such processes are explained below. There are three main stages of cellular respiration. ENE1L5 EK ENE1L7 EK Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.