Food Chain Definition Geography

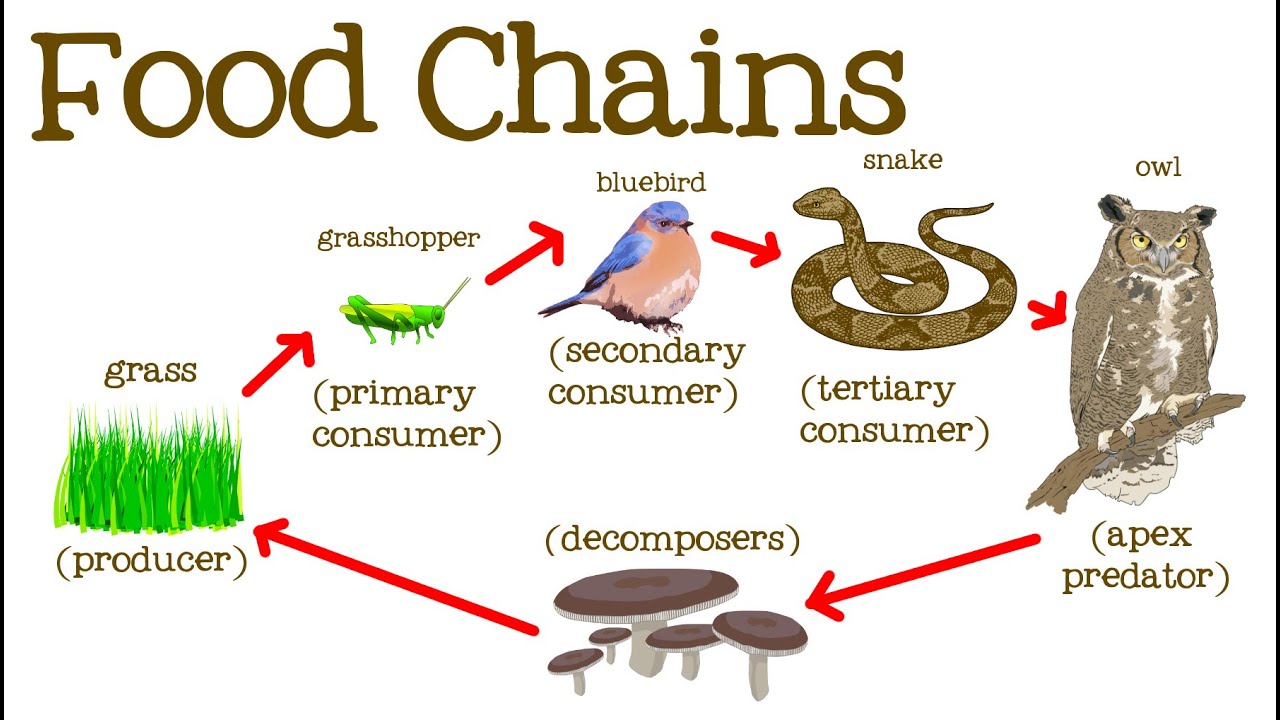
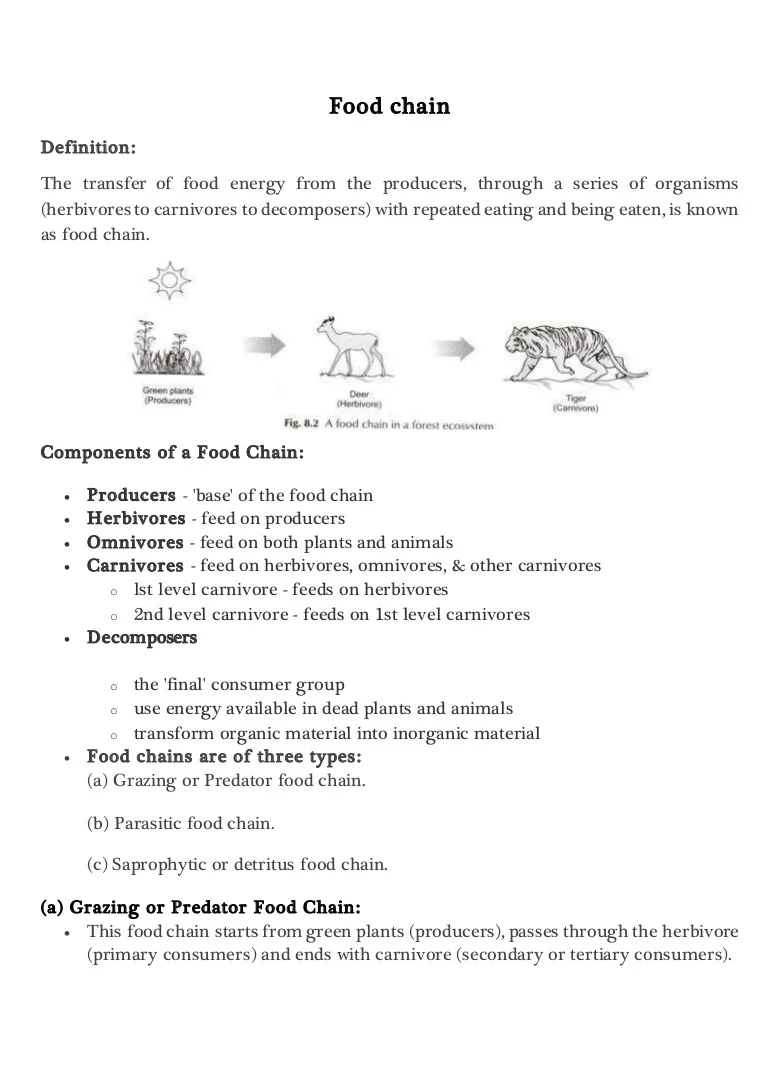
Food Chain - A food chain is the series of organisms showing feeding relationships.
Food chain definition geography. Plants which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis are the primary food source. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific Technical Terms 6E Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. A food chain often ends with a predator or an omnivore like humans.
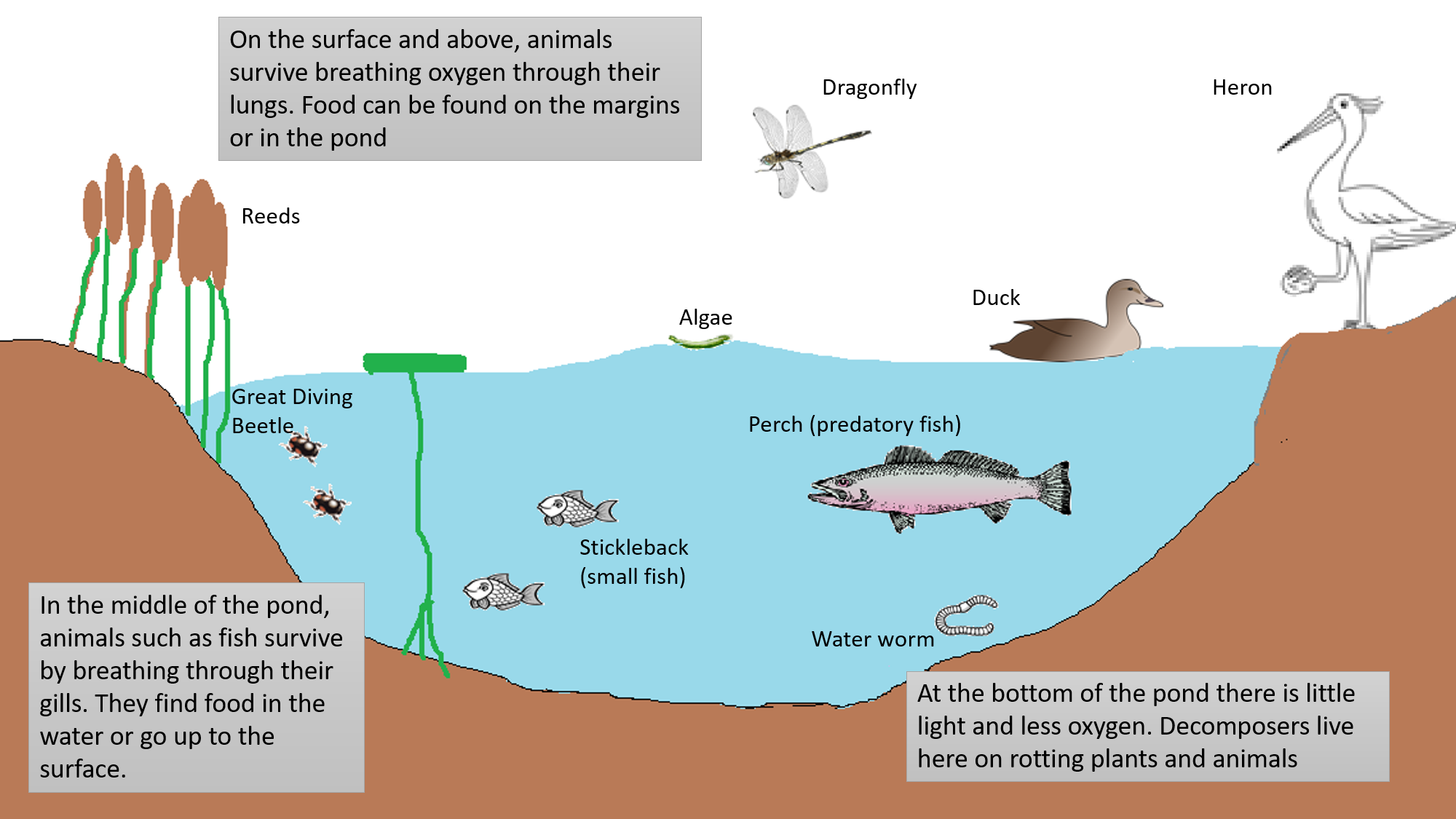
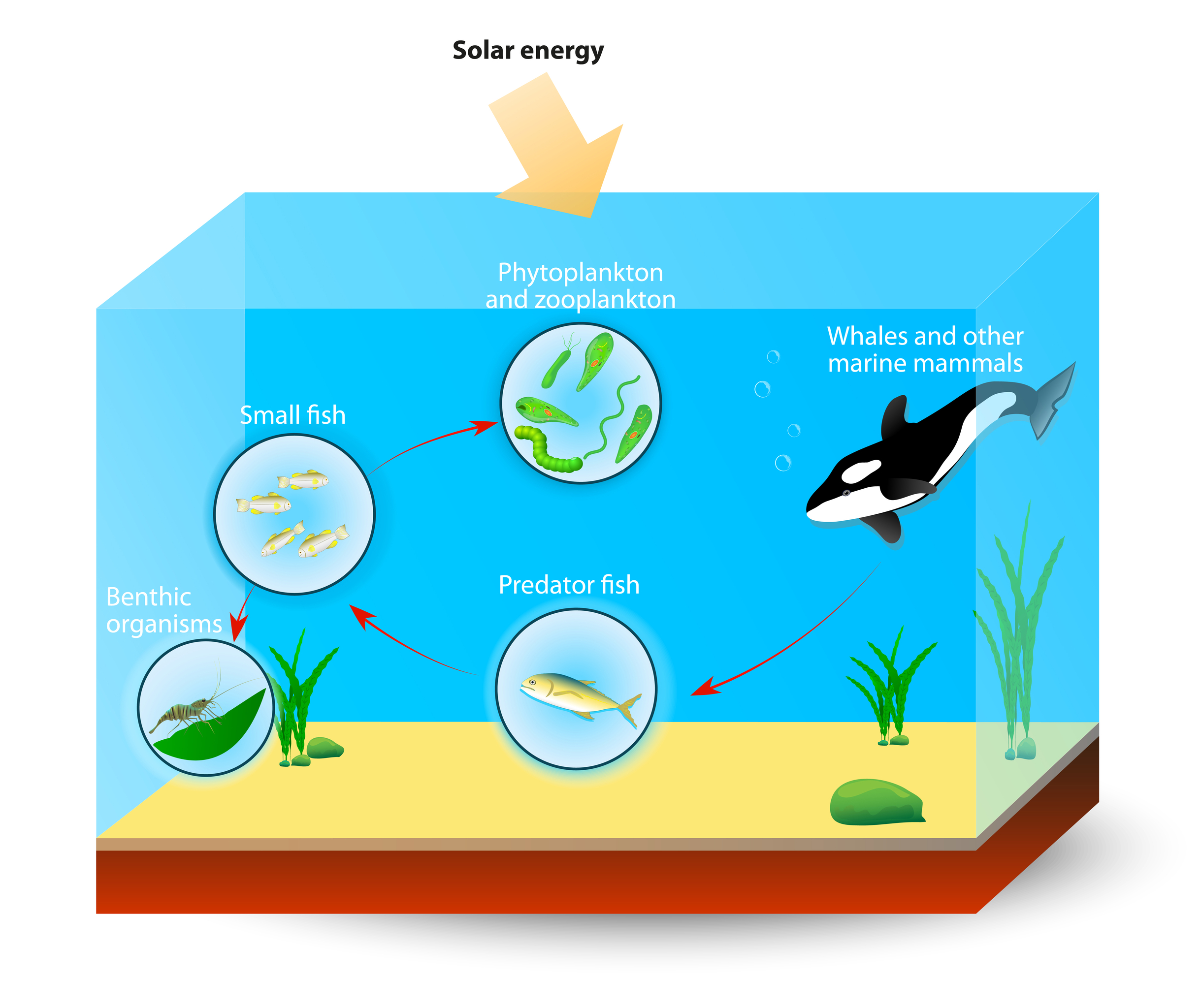
Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Plants are at the beginning of every food chain that involves the sun. It starts with energy from the sun.
Some Apex predators include sharks lions and owls. Inefficient food supply chains generate a larger amount of waste in terms of food that is lost during harvesting storage transportation preparation distribution and consumption. For example grass produces its own food from sunlight.
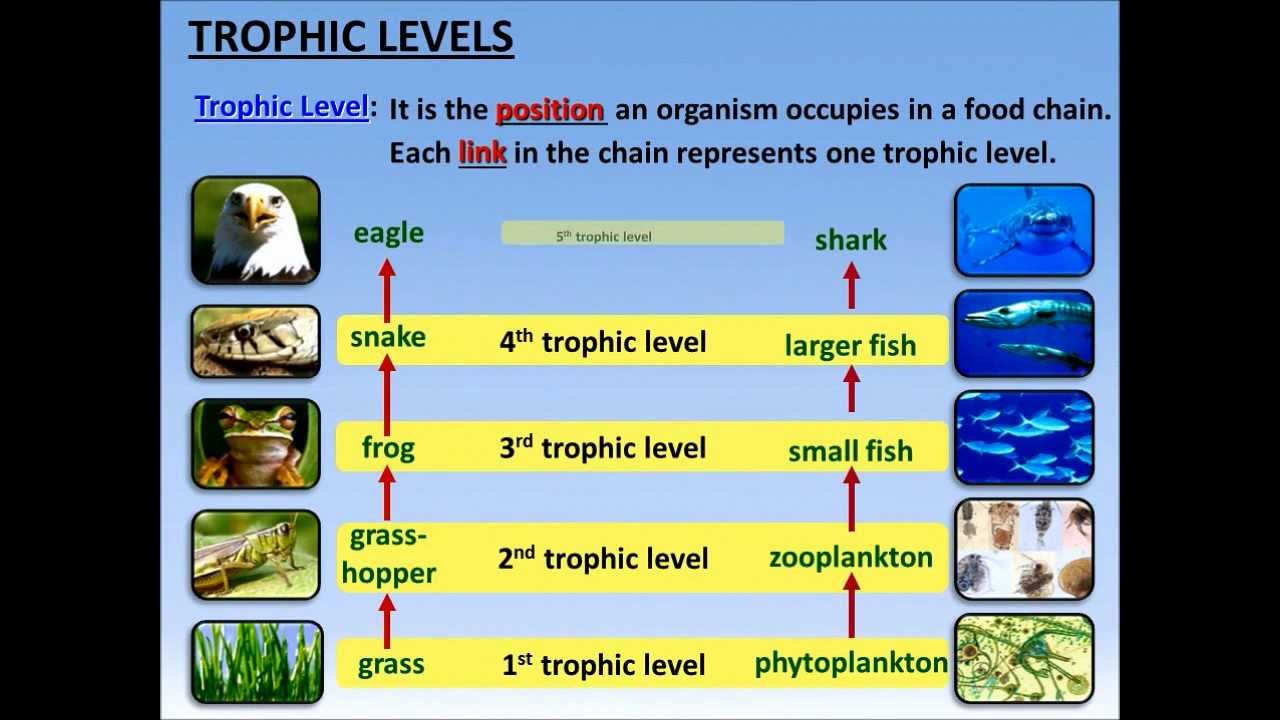
Many food chains make up a food web. This information should not be considered complete up to date and is not. It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a producer.
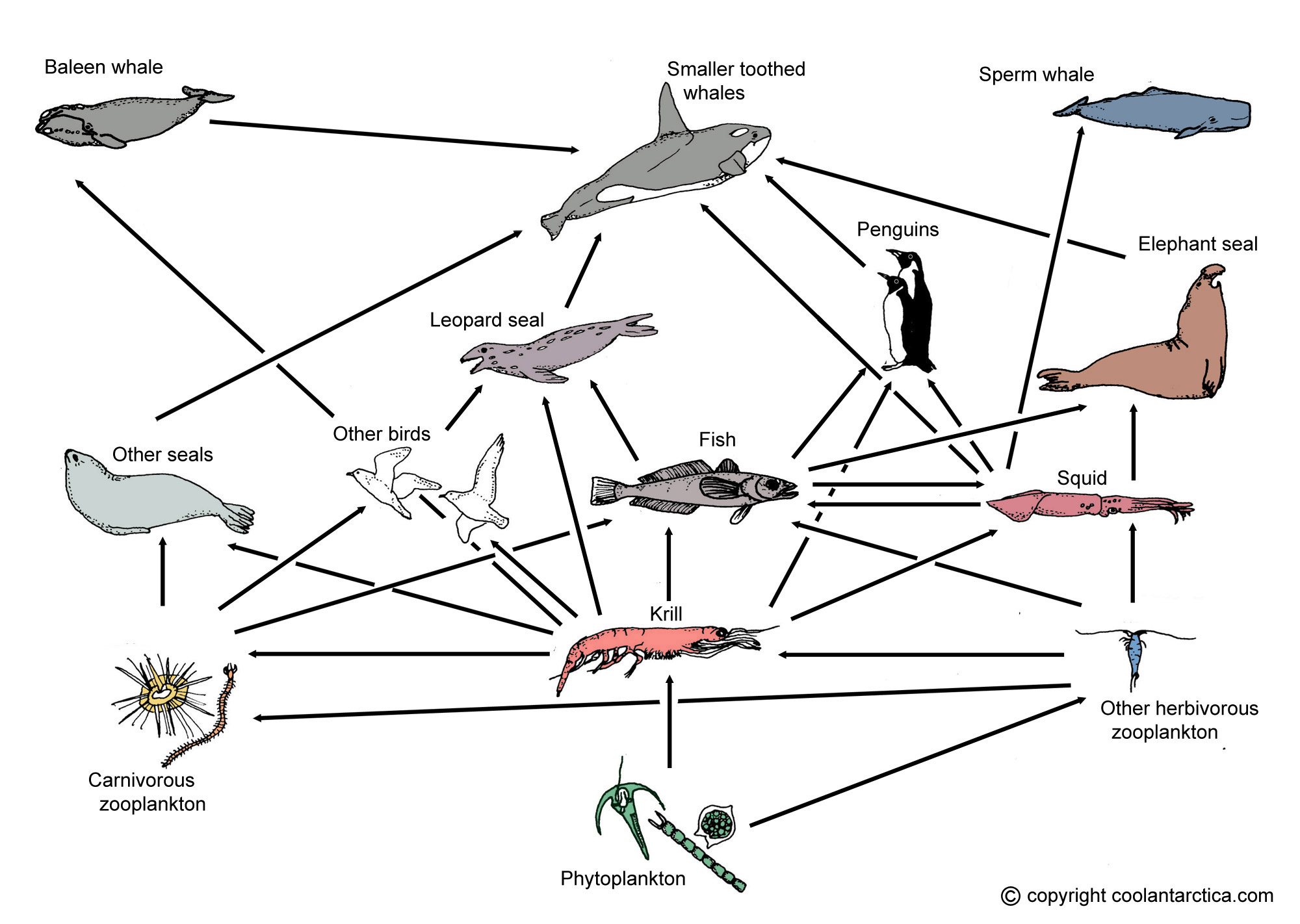
When two or more than two types of food chains get connected or interlinked with each other then they form a food web. The definition of food web is a model of food chains that intersect and show what eats what. Food web is a connection of multiple food chains.
Food losses are the highest for fruits and vegetables where on average 50 to 60 of all the production is lost along the supply chain implying that only 40 to 50 of what is being harvested end up. The arrow means is eaten by and shows the flow of matter and energy along the food chain. The other creatures are producers they get their energy from the sugars glucose made by consumers.