Marine Animals Definition Biology

Spongin- flexible protein fibers.
Marine animals definition biology. Marine biologist definition is - a scientist who studies life in the sea. Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea. Most marine biologists choose a specialty field such as phycology ichthyology invertebrate zoology marine mammalogy fishery biology marine biotechnology marine microbiology or marine ecology.
So a marine biologist studies. Marine biologists study a wide variety of aquatic organisms from microscopic plankton to massive whales. The scientific study of organisms living in or dependent on the oceans.
Marine life definition biology. A marine biologist is someone who is interested in learning and studying marine organisms and what their lives are like in their natural habitats. The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist.
As a marine biologist you may study a wide range of topics from the behavior physiology and ecology of specific groups of organisms to the interactions between human activity and aquatic environments. Marine biologists may have many different jobs including working with marine mammals eg a dolphin researcher studying the seafloor researching algae or even working with marine microbes in a lab. Spicules- skeletal elements that support a sponge.
It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world. This type of pollution occurs when human activities notably the use of fertilizer on farms lead. Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge.
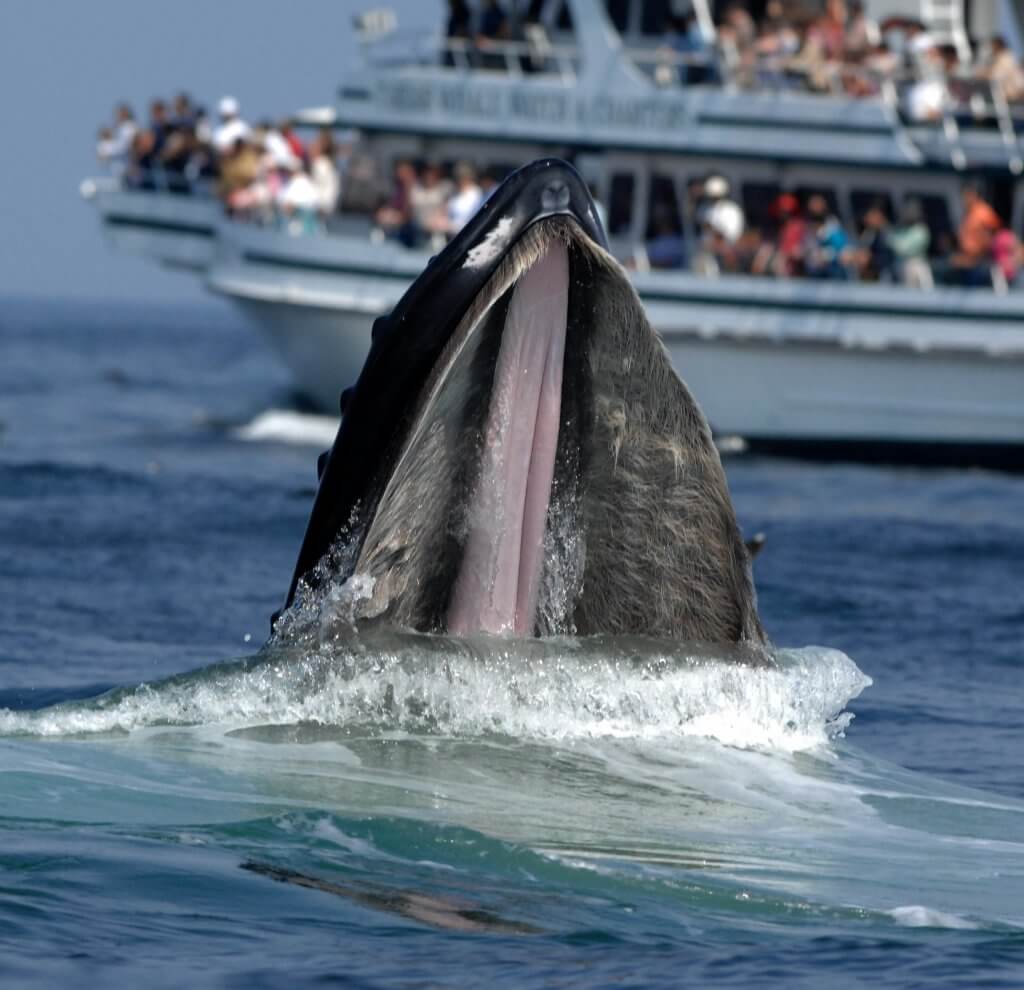
Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water. Osculum- large opening that lets water out. Marine biologists study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical physical and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms.